What is citrus psylla?
Citrus psylla, scientifically known as Diaphorina citri, is a tiny brown insect which sucks cell sap from leaves, tender shoots and flower buds.
 | 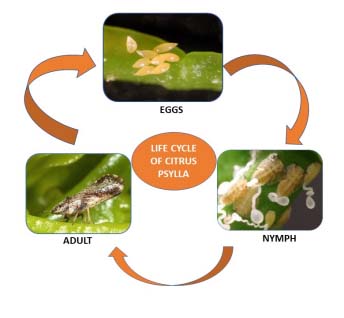 |
- Eggs– Female lay eggs on the tips of growing shoots, between and near the unfurling leaves which are almond-shaped, thicker at the base, and taper towards the opposite end. One female can lay 500- 800 eggs during their life cycle. The egg hatches in 4- 8 days.
- Nymph– Citrus Psylla have five nymphal instars. Nymph are Light yellow to dark brown with pair of red compound eyes measuring 0.25 mm- 1.7 mm (0.01- 0.07 in.) in length which depend on the nymphal instar. They have well-developed, large wing pads in fifth- instar.
- Adults- The adults are mottled, yellowish-brown body with brown legs and a light brown head with greenish-white on the ventral region. Adults measure 2.5 – 4 mm (0.12 – 0.16 in.) in length. The wings are transparent with white spots or light-brown with a broad, longitudinal beige band in the center. Due to a whitish, waxy secretion they have dusty appearance.
How does it damage the plant?
- Mostly the damage on plants is done by nymph and adult by sucking the sap from the leaves, young shoots, buds, flowers and tender branches.
Symptoms-
- Young shoots of the affected plants result in stunting and twisting so that the growing tips present a rosette appearance and later on due to heavy infestation the twigs entirely result in die back.
- Leaves are badly curled and drop prematurely.
- Excessive de-sapping consequently affects the fruit set seriously.
- The affected fruits appear small and fall prematurely.
- Citrus Psyllid secrete honeydew which results in the growth of the sooty mould fungus.
- Citrus Psylla also cause the Citrus greening disease.
 |  |
| https://www.krishisewa.com/images/articles/2016/psyllid-pests-4.jpg | http://entnemdept.ufl.edu/creatures/citrus/acpsyllid.htm |
Period of Severe infestation-
- Feb – March
- June – July
- October – November
Management-
| Mechanical & Cultural Control | Biological Control | Chemical Control |
| Prune the affected and dried shoot and modify the canopy structure which help in maximum light interception.Collateral host like Curry leaf (Murraya koengii) plant should not be grown in the vicinity of citrus orchard as it serves as a breeding ground for citrus psylla. | Lace wings and lady bird beetles are important natural enemies of Citrus psylla.Two releases of Mallda desjardinsi @ 30 larvae/tree in each flushing season reduces the incidence levels of Citrus psylla. | Spray Neem oil 5ml per liter water.Spray Imidacloprid 30.5% SC @ 0.5 ml per liter water i.e., 200 liter per acre and PHI 15 days.Foliar spraying of insecticides for effectively controlling population of the insect.Profenofos 50 EC @ 2ml per liter of water Thiamethoxam 30% FS @ 0.5 ml per liter of water |
Reference- (Citrus Psylla)-
- Gebreslasie. A. and Meresa., H. 2018. Identification of insect and disease associated to citrus in Northern Ethiopia. African Journal of Microbiology Research. 12(13); 312-320
- Kumar. R., Ghosh. A., Das. A. and Meena. R. 2015. Major Diseases and Insect Pests Problems of Mandarin Orange and Their Management in NEH Regions of Darjeeling and Sikkim. Popular Kheti, 3(3): 128-137
- https:/https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/18615/
- www.citrusres.com/system/files/documents/production-guidelines/Ch%20310%20Psylla%20-%20Jan%202012.pdf
- https://idtools.org/id/citrus/pests/factsheet.php?name=Asian%20citrus%20psyllid
- http://nhb.gov.in/pdf/fruits/citrus/cit008.pdf








