What is Shoot and Fruit Borer?
The name only indicates it’s meaning, the larvae which will bore on shoot and fruit. It is one of the major pests of jackfruit in India. The humid tropics are most favourable for the growth and development of shoot and fruit borer.
Scientific Name- Diaphania caesalis

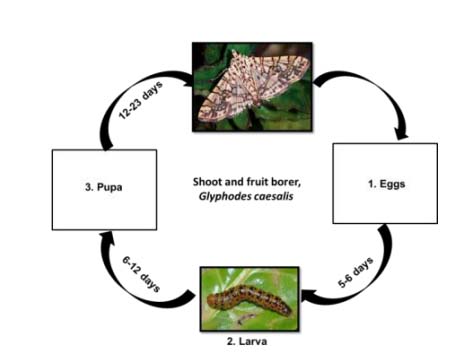
Life cycle-
- Eggs- Females lay eggs on flower buds. It takes 2 – 3 days for the eggs to hatch and form neonate.
- Larva- Newly hatched larvae are very minute, with whitish brown body. The caterpillar is reddish brown with black spots and bores into the tender shoots and developing fruits, occasionally causing substantial damage. The caterpillar undergoes four molts before it enters pupation. This period takes 5 – 6 days.
- Pupae- The pupation take place on the lower side of the leaf or twisted dried leaf or inside the tunnel dug by adult to protect the eggs. Pupa looks reddish brown in colour. The pupation period varies from 12-23 days.
Adult- The adults are medium sized, whitish brown in colour with grey coloured elliptical patterns on the forewings.
- The life cycle is completed around 25 – 44 days depending on the season.
How does Shoot and Fruit borer damage?
- The larva mines into the shoot or apical buds and feeds on internal content.
- A mass of excreta can be seen outside of the entry hole.
- It is also found to feed on leaves and lower buds.
- Affected parts wilt and gets dried up.
- In severe conditions, the fruits rot and premature fruit drop can be observed.
- The caterpillar attacks the tip of tender shoot of mature tree and leads to its wilting.

How to manage Shoot and Fruit borer?
| Cultural Method | Chemical Control |
| Removal and destruction of the affected shoots, lower buds, and fruits in the initial stage of attack reduces the infestation of the pest. | Foliar Spray:Spinosad 45% EC @0.4 ml/litre.Emamectin Benzoate 5% SG @1g/litre.Imidachloropid 17.8% SL @0.5 ml/litre.Fenitrothion 50 EC @2 ml/litre. |
References–
- https://niphm.gov.in/IPMPackages/Jackfruit.pdf
- Image source: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Kallekkattil-Soumya/publication/305809889_Occurrence_of_Jack_shoot_and_fruit_borer_Diaphania_caesalis_Walker_Pyralidae_Lepidoptera_in_Kerala_India/links/57a2d58608ae5f8b258cb76b/Occurrence-of-Jack-shoot-and-fruit-borer-Diaphania-caesalis-Walker-Pyralidae-Lepidoptera-in-Kerala-India.pdf
- Image source: http://www.agritech.tnau.ac.in/horticulture/horti_fruits_jack.html








